Question 1
a. Present a comparative overview among the different levels of abstraction of a database management system. 06
Ans:
- Physical level: The lowest level of abstraction describes how the data are actually stored. The physical level describes complex low-level data structures in detail.
- Logical level:
Describes data stored in database, and the relationships among the data. The conceptual schema describes the design of a database at the conceptual level. Conceptual level is also known as logical level.
type instructor = record ID : string; name : string; dept_name : string; salary : integer; end; - View level: Application programs hide details of data types. Views can also hide information (such as an employee’s salary) for security purposes.
b. What is Data Model? Write down the name of two existing data model.04
Ans: Underlying the structure of a database is the data model: a collection of conceptual tools for describing data, data relationships, data semantics, and consistency constraints. A data model provides a way to describe the design of a database at the physical, logical, and view levels. Among four different categories, two models are:
- Relational Model: The relational model uses a collection of tables to represent both data and relationships among those data.
- Entity-Relationship Model: The entity-relationship (E-R) data model uses a collection of basic objects to design a database.
Question 2
a. Find the Primary Key for all the tables with brief justification of the reason to choose the attribute in the primary key: 06
order (order_id, product_id, quantity, unit, unit_price, discount, bill)
warehouse_stock (warehouse_id, product_id, quantity, last_updated)
order_details(customer_id, product_id, warehouse_location, order_date, quantity, shipping status)
Ans:
1. order
Primary Key: (order_id, product_id)
Justification: Each order may include multiple products. Thus, the combination of order_id and product_id uniquely identifies every product entry within an order.
2. warehouse_stock
Primary Key: (warehouse_id, product_id)
Justification: A product can be stored in multiple warehouses. The pair (warehouse_id, product_id) uniquely identifies each product stored in a specific warehouse.
3. order_details
Primary Key: (customer_id, product_id, order_date)
Justification: A customer can order the same product on different dates. Hence, (customer_id, product_id, order_date) uniquely represents each order transaction.
b. Write the query in SQL to create the orderrelation.04
Ans:
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id INT,
product_id INT,
quantity INT,
unit VARCHAR(10),
unit_price DECIMAL(10,2),
discount DECIMAL(5,2),
bill DECIMAL(10,2),
PRIMARY KEY (order_id, product_id)
);Question 3
a. Consider the following relational schema for an online grocery shop database.02+03+03
customer (customer_id, customer_name, city, age)
product (product_id, product_name, price, category)
order (order_id, customer_id, product_id, quantity, order_date)
stock (product_id, warehouse, quantity_available)
Write relational algebra expressions for each of the queries:
- Retrieve the customers who have ordered products in the “Electronics” category.
- List the product IDs that have been ordered by customers from “Dhaka” but are not available in the warehouse “Central Warehouse”.
- Retrieve the names of warehouses that stock only products from the “Clothing” category.
Ans:
b. What is Data Manipulation Language?02
Ans: A data-manipulation language (DML) is a language that enables users to access or manipulate data as organized by the appropriate data model. It is a subset of SQL used to retrieve, insert, update, and delete data in a database. It focuses on manipulating data within existing tables, not defining the schema (which is done by DDL).
Question 4
Consider the following relational schema for an online grocery shop database.
customer (customer_id, customer_name, city, age)
product (product_id, product_name, price, category)
order (order_id, customer_id, product_id, quantity, order_date)
stock (product_id, warehouse, quantity_available)
a. Write query in SQL for each of the following queries: 03+04+03
- Show the customer IDs in the descending order who have ordered products in the “Electronics” category.
- Find the names of products that have been ordered by customers from the city “Dhaka” and display the total quantity ordered for each of those products.
- List the Product ID and Product Name of products that are currently out of stock in the “Central Warehouse”.
Ans: 1.
SELECT DISTINCT customer_id
FROM `order`
NATURAL JOIN product
WHERE category = 'Electronics'
ORDER BY customer_id DESC;SELECT DISTINCT product_name, quantity
FROM `order`
NATURAL JOIN product
NATURAL JOIN customer
WHERE city = 'DHAKA';SELECT DISTINCT product_id, product_name
FROM stock
NATURAL JOIN product
WHERE quantity_available = 0 and warehouse = "Central Warehouse";Question 5
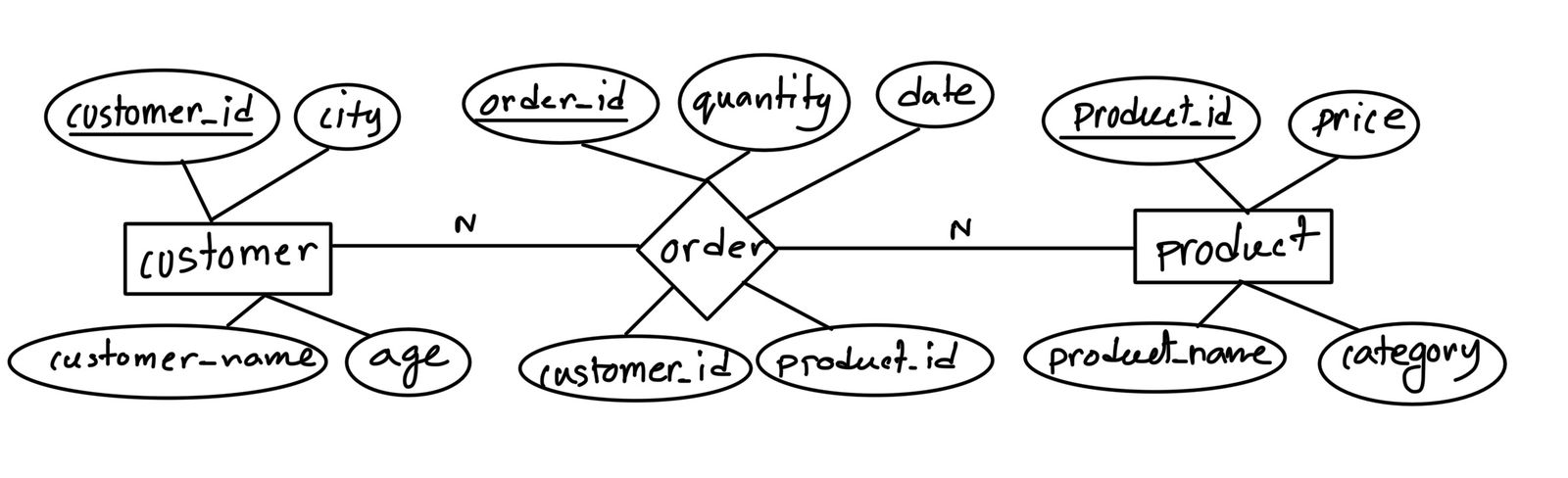
a. Draw the E-R Diagram of a online grocery shop database considering three entities: customer, product, order.10
Ans: