Question 1
a. Briefly describe the operation of Data Encapsulation using a diagram.4
Ans: To send a message from one process to another, the transport-layer protocol encapsulates and decapsulates messages. Encapsulation happens at the sender site. When a process has a message to send, it passes the message to the transport layer along with a pair of socket addresses and some other pieces of information, which depend on the transport-layer protocol. The transport layer receives the data and adds the transport-layer header. The packets at the transport layer in the Internet are called user datagrams, segments, or packets, depending on what transport-layer protocol we use. In general discussion, we refer to transport-layer payloads as packets1.
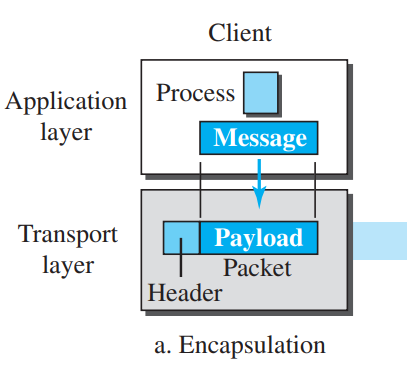
b. 4
- Differentiate between guided media and unguided media.
For guided media, electromagnetic waves are guided along a solid medium, such as copper twisted pair, copper coaxial cable, and optical fiber. For unguided media, wireless transmission occurs through the atmosphere, outer space, or water2. - Short notes on Baud Rate, Half-duplex, Bridge/Switch, BPSK.
- Baud rate is the rate at which the number of signal elements or changes to the signal occurs per second when it passes through a transmission medium.
- With half-duplex transmission, only one of two stations on a point-to-point link may transmit at a time.
- Switches/bridges are Data Link Layer (Layer 2) devices that connect network segments or devices by filtering and forwarding data frames based on their physical (MAC) addresses.
- In BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying), the phase of the carrier signal is shifted to represent data2.
c. 4
- What are the differences between thermal noise and cross-talk?
Thermal noise is an internal disturbance caused by the random thermal motion of electrons within a conductor due to ageing, which exists in all electronic devices regardless of signal presence. Cross-talk is an external interference where a signal from one transmission line electromagnetically couples with and disrupts a signal in an adjacent line. - Given a receiver with an effective noise temperature of and a bandwidth. Find out the thermal noise level at the receiver’s output.
Thermal noise in watts present in a bandwidth of can be expressed as :
d. Solve the following problems:6
-
There is a channel with that has capacity and the bandwidth of the given channel is . What signal-to-noise ratio is required to achieve this capacity (assuming that white thermal noise exists)?
Using Shannon’s formula,Thus, required signal-to-noise ratio, .
-
A digital signaling system is required to operate at . If a signal element encodes a word, what is the minimum required bandwidth of that channel?
Using Nyquist’s formula,Thus, required minimum bandwidth is .
e. What is socket address? List out the application of socket addressing.2
Ans: A transport-layer protocol in the TCP suite needs both the IP address and the port number, at each end, to make a connection. The combination of an IP address and a port number is called a socket address1. Applications of socket addressing includes:
- Process Identification
- Client-server communication
- Data Multiplexing
- Connection Management
Question 2
a. We assume there are 15 senders. These senders are to be multiplexed into a single communication line/channel. Each sender are bursty and each can generate data rate at . Certain cases, Some are idle and some are active. Under-these circumstances, find out the minimum channel capacity for the following conditions:6
Ans:
- 15 senders are active under Synchronous Time Division Multiplexing.
Minimum channel capacity, - Maximum 1=5 senders are active under Statistical Time Division Multiplexing.
Minimum channel capacity, - 15 senders are active under Synchronous Time Division Multiplexing.
Minimum channel capacity,
b. What is called controlled access? What are the differences between reservation and polling method? Using a diagram, explain the token parsing method. 4
Ans: In controlled access, the stations consult one another to find which station has the right to send. A station cannot send unless it has been authorized by other stations.
In Reservation, a station must book a specific time slot or channel resource in advance before transmitting data, treating the medium as a scheduled resource. Whereas, in Polling, a central controller functions as a master that sequentially invites each secondary station to transmit, allowing access only when a station is addressed1.
Token Parsing
In the token-passing method, the stations in a network are organized in a logical ring. In other words, for each station, there is a predecessor and a successor. The predecessor is the station which is logically before the station in the ring; the successor is the station which is after the station in the ring. The current station is the one that is accessing the channel now. The right to this access has been passed from the predecessor to the current station. The right will be passed to the successor when the current station has no more data to send.
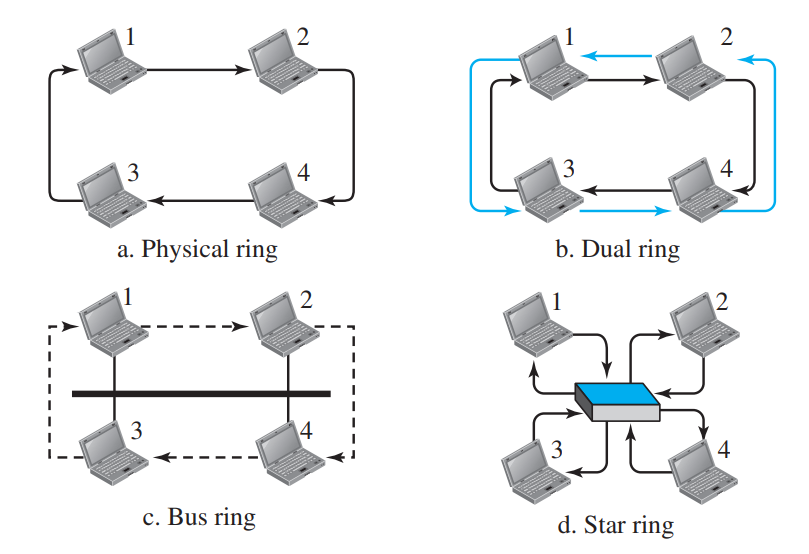 Figure: Logical ring and physical topology in token-passing access method
Figure: Logical ring and physical topology in token-passing access method
c. For a wireless network, there are multiple senders and receivers. Under the slot, the sender tries to send a frame. Currently, the value of is (each slot carries ). Given, is , and distance between sender and receiver is meter where velocity is . Find out the total time that is required to get positive acknowledgement from the receiver to sender. 5
Ans:
d. A slotted ALOHA network transmits frames using a shared channel with a bandwidth. Under this circumstances, deduce the throughput for the following cases:5
- 1200 frames/second
- 600 frames/second
- 300 frames/second
Ans: The frame transmission time is,
- 1200 frames/second
- 600 frames/second
- 300 frames/second
Question 3
a. Briefly describe the operation of Data Encapsulation using a diagram. 5
Ans: To send a message from one process to another, the transport-layer protocol encapsulates and decapsulates messages. Encapsulation happens at the sender site. When a process has a message to send, it passes the message to the transport layer along with a pair of socket addresses and some other pieces of information, which depend on the transport-layer protocol. The transport layer receives the data and adds the transport-layer header. The packets at the transport layer in the Internet are called user datagrams, segments, or packets, depending on what transport-layer protocol we use. In general discussion, we refer to transport-layer payloads as packets.

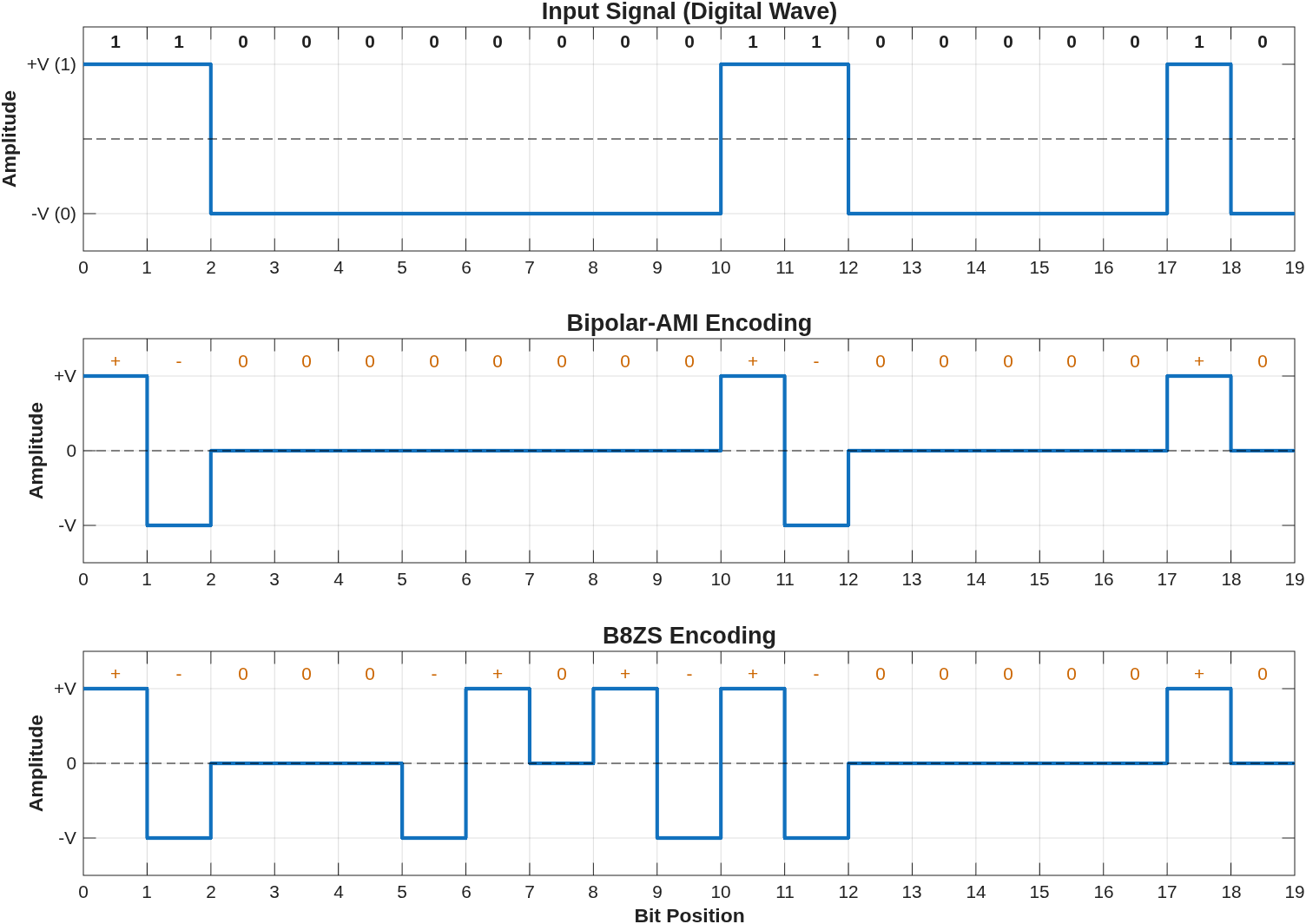
b. Find the digital encoding for the following digital data: 6
- Bipolar-AMI (most recent preceding 1 bit has negative edge).
- B8ZS
c. 4
-
Short note on: Pulse code modulation.
Pulse code modulation (PCM) is based on the sampling theorem: If a signal is sampled at regular intervals of time and at a rate higher than twice the highest signal frequency, then the samples contain all the information of the original signal. The function may be reconstructed from these samples by the use of a lowpass filter. -
Fill the table:
| Type | Frequency Range |
|---|---|
| Microwave | |
| Omni-directional | |
| Infrared |
d. 5
- What is Data Encoding? List out the techniques of digital data to analog signal.
Data encoding is the process of converting data from one form into another format using a specific set of rules or schemes. Both analog and digital information can be encoded as either analog or digital signals. The particular encoding that is chosen depends on the specific requirements to be met and the media and communications facilities available.- Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK)
- Frequency Shift Keying (FSK)
- Phase Shift keying (PSK)
- Explain the difference between NRZ-L and NRZI.
| NRZ-L (Level) | NRZ-I (Invert) |
|---|---|
| The level of the voltage determines the bit value. | The transition (or lack of it) at the beginning of the bit interval determines the bit value. |
A positive voltage represents 0 and a negative voltage represents 1 (or vice versa). | A transition (change in voltage) represents 1. No change represents 0. |
| Loses synchronization during long strings of 0s or 1s (voltage stays constant). | Loses synchronization only during long strings of 0s (no transitions occur). |
| Sensitive: If the wires are swapped (polarity reversed), all 0s become 1s and vice versa. | Robust: Swapping wires has no effect because the receiver looks for changes, not absolute levels. |
Question 4
a. As a network administrator, you are responsible to design a network according to given IP Address. For example, The given IP address is: 14
You are asked to design:
- Create 16 sub-networks and list out those networks.
IP Address =
Default CIDR =
Sub-Networks = 16 Increment per network =
- Find the total usable IP Addresses for the hosts under those networks
- Find the network address of the network.
- Find the broadcast address of the network.
- Find the host address of network.
- Find the last host address of network.
- Find the host address of network.
b. 3
- Define Unicast, Multicast, Broadcast addresses with example.
In a unicast transmission, all stations will receive the frame, the intended recipient keeps and handles the frame; the rest discard it.
Example: 4A:30:10:21:10:1A
In a multicast transmission, all stations will receive the frame, the stations that are members of the group keep and handle it; the rest discard it. Example: 47:20:1B:2E:08:EE
In a broadcast transmission, all stations (except the sender) will receive the frame and all stations (except the sender) keep and handle it.
Example: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF - From the following addresses find the unicast, multicast, and broadcast address.